Artificial Intelligence (AI) is advancing each year, and by 2025, one of the most promising methods to enhance AI reasoning is through Chain of Thought (CoT) Prompting. This innovative technique enables AI to think in a step-by-step manner, mirroring human problem-solving. Instead of providing brief, direct responses, AI dissects complex queries into smaller components, leading to more precise and insightful answers.
This guide will empower you with a comprehensive understanding of Chain of Thought Prompting (CoT), how it works, and its benefits in 2025. Whether you're a novice or an expert in AI, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to leverage CoT for enhanced AI performance.
What is Chain of thought prompting?
Chain of Thought (CoT) prompting is a method used to help AI think step by step before giving an answer. Normally, AI models give quick responses based on patterns they have learned. But with Chain of Thought prompting, the AI explains its reasoning before reaching a final answer. This helps improve accuracy, especially for complex problems like math, logic, and decision-making.
How It Works
Instead of just asking the AI a question, Chain of Thought prompting encourages it to break the problem into smaller steps.
For example, if you ask:
"If John has 3 apples and buys 5 more, how many does he have in total?"
A normal AI might just say "8." But with CoT prompting, it would respond like this:
- John starts with 3 apples.
- He buys 5 more apples.
- To find the total, we add 3 + 5.
- The final answer is 8 apples.
This systematic approach ensures that the AI provides more reliable and logical answers. It is particularly beneficial in coding, problem-solving, and real-world decision-making. By compelling AI to articulate its thought process, Chain of Thought prompting enhances clarity and reduces errors, instilling a sense of trust in its responses.
Types of Chain of Thought Prompting
1. Standard Chain of Thought Prompting
This is the basic way of using chain of thought (CoT) prompting. It asks the AI to explain its reasoning step by step. Instead of giving a direct answer, the AI first breaks the problem into smaller parts, solves each part, and then combines the answers.
For example, if the AI is asked, "If a train travels 60 km in one hour, how far will it travel in 3 hours?" the AI will answer like this:
- The train moves 60 km in one hour.
- In two hours, it will move 60 km × 2 = 120 km.
- In three hours, it will move 60 km × 3 = 180 km.
This step-by-step process helps improve accuracy, especially for math and logic problems.
2. Self-Consistency Chain of Thought Prompting
This method improves accuracy by asking the AI to think of multiple solutions and then choose the best one. Instead of giving just one answer, the AI comes up with different possible solutions and selects the most consistent one.
For example, in a reasoning problem, the AI might first solve the problem three times in different ways. Then, it will compare the answers and choose the one that appears most frequently. This reduces mistakes and makes the AI's answer more reliable.
3. Tree of Thought Prompting
This method is useful for complex decision-making. Instead of solving a problem in one straight line, the AI explores different possible paths, like branches of a tree. It checks which path leads to the best answer.
For example, if the AI is asked, "What is the best way to spend $100 wisely?" it might first consider different categories like:
- Saving
- Investing
- Buying essential items
- Spending on entertainment
Then, it will explore each option further and compare them before making a final decision. This method helps in creative problem-solving.
4. Least-to-Most Chain of Thought Prompting
This type of prompting helps with difficult problems by starting with the simplest part first. Instead of solving everything at once, the AI breaks the question into small, easy steps and works its way up.
For example, if the AI is solving a complicated math word problem, it will first answer the simplest question in the problem. Then, it will build on that answer step by step until the final solution is reached. This method is helpful for learning and understanding tough concepts.
5. Recall-Augmented Chain of Thought Prompting
In this method, the AI looks back at previous information before answering a question. This is useful for problems that require memory, such as history questions or long conversations.
For example, if the AI is asked, "Who was the first president of the United States, and why was he important?" It will first recall facts about George Washington and then explain why he was important. This approach ensures the AI provides more accurate and detailed responses.
6. Analogical Chain of Thought Prompting
This method uses comparisons to make complex ideas easier to understand. If a topic is difficult, the AI finds a similar, simpler example to explain it.
For example, if someone asks, "How does blockchain work?" the AI might say:
"Think of blockchain like a notebook where each page is a record of transactions. Once a page is full, you add another page, and the pages are linked together. No one can change old pages, making the notebook secure."
Using analogies helps make new or difficult topics easier to understand.
7. Decomposed Chain of Thought Prompting
This method is useful when a problem has many parts. Instead of answering everything at once, the AI breaks the question into smaller pieces and answers each part separately.
For example, if the AI is asked, "What are the causes and effects of climate change?" it will first answer:
- Causes of climate change (e.g., pollution, deforestation)
- Effects of climate change (e.g., rising temperatures, extreme weather)
Then, it will combine the answers into a full response. This makes explanations clearer and more organized.
Benefits of Chain of Thought Prompting
1. Better Problem Solving
Chain of Thought (CoT) prompting is a powerful tool that empowers AI to break down complex problems into manageable steps. Instead of leaping to the answer, it fosters a methodical thinking process. This is beneficial in various domains, from mathematical conundrums to real-world decision-making. For instance, when faced with a challenging math problem, CoT prompting guides the AI to elucidate each calculation, leading to reduced errors and clearer solutions.
2. Improved Accuracy
When an AI follows a step-by-step approach, it is less likely to make mistakes. Without CoT prompting, an AI might guess answers based on patterns instead of reasoning. But with CoT, the AI carefully considers each step before making a decision. This is especially helpful in fields like medicine, law, and coding, where small mistakes can lead to big problems.
3. Easier to Understand Explanations
CoT prompting makes AI responses more detailed and easy to follow. Instead of giving short or confusing answers, the AI explains its reasoning clearly. For example, if someone asks why the sky is blue, a CoT-prompted AI will explain the science behind it step by step, making it easier to understand. This is great for learning new things and improving education.
4. Better Handling of Complex Tasks
Some tasks require multiple steps to complete. Without CoT prompting, an AI might struggle with multi-step reasoning. For example, if an AI is asked to summarize a long article while keeping the key points, CoT helps it break the article into sections, understand each part, and then create a proper summary. This makes AI better at handling complex requests.
5. Encourages Logical Thinking
CoT prompting instills in AI a human-like approach to thinking. Instead of rote memorization, it learns to dissect information logically. This is particularly crucial in scenarios where AI needs to compare different options or make predictions. For instance, when tasked with suggesting the best marketing strategy for a business, a CoT-driven AI will weigh the merits of various approaches before delivering a thoughtful response.
6. Reduces Bias in AI Responses
At times, AI can make biased decisions due to overreliance on patterns from past data. CoT prompting plays a crucial role in mitigating bias by encouraging the AI to justify its reasoning. If an answer appears unfair or incorrect, users can scrutinize the AI’s logic and rectify any errors. This enhances the transparency and trustworthiness of AI responses.
5 Major Use cases of Chain of Thought Prompting
1. Helping AI Solve Math Problems
Chain of Thought (CoT) prompting helps AI break down math problems step by step. Instead of giving a direct answer, the AI explains its thinking process. For example, if the problem is "What is 25 times 4?", the AI can first break it into smaller steps:
- Step 1: 25 is the same as 20 + 5.
- Step 2: Multiply 20 by 4 to get 80.
- Step 3: Multiply 5 by 4 to get 20.
- Step 4: Add 80 and 20 to get 100.
By using this method, AI improves its accuracy in solving complex math problems, as it reduces errors caused by skipping steps.
2. Improving AI’s Logical Thinking
When AI is asked tricky logic questions, Chain of Thought prompting helps it think step by step. For example, if the AI is given this puzzle:
"If a rooster lays an egg on a roof, which side will it roll down?"
Using CoT prompting, the AI will reason through it:
- Step 1: Roosters are male chickens.
- Step 2: Only female chickens (hens) lay eggs.
- Step 3: Since a rooster cannot lay eggs, the question is a trick question.
With this approach, AI avoids making wrong assumptions and improves its ability to solve riddles and logical problems.
3. Helping AI Answer Long and Complex Questions
Sometimes, a question may have multiple parts. Without thinking step by step, AI may miss important details. For example, if someone asks:
"How does the internet work, and why do we need Wi-Fi?"
Using CoT prompting, AI will break it down:
- Step 1: Explain how the internet connects computers worldwide.
- Step 2: Explain how data travels through cables and wireless networks.
- Step 3: Explain that Wi-Fi allows devices to connect to the internet without cables.
By thinking step by step, AI provides a complete and clear answer instead of skipping important details.
4. Helping AI Code More Accurately
When AI writes code, mistakes can happen if it does not think step by step. Chain of Thought prompting helps AI plan before coding. For example, if AI is asked to write a program to find the largest number in a list, CoT prompting helps like this:
- Step 1: Start with the first number in the list.
- Step 2: Compare it with the next number.
- Step 3: If the next number is bigger, update the largest number.
- Step 4: Repeat this for all numbers in the list.
- Step 5: Print the largest number.
This method helps AI write better code and avoid errors by carefully thinking through each step.
6. Helping AI Make Better Decisions
AI sometimes needs to make choices based on given information. For example, if AI is helping a doctor decide whether a patient needs a test for diabetes, CoT prompting helps like this:
- Step 1: Check if the patient has symptoms like frequent thirst and tiredness.
- Step 2: Check the patient’s medical history to see if they are at risk.
- Step 3: Check if the patient’s family members have diabetes.
- Step 4: If symptoms and risks are high, recommend a diabetes test.
By thinking step by step, AI makes better decisions instead of guessing.
Also Read: Midjourney V5: Create Stunning AI Images with the Latest Version
Limitations of Chain of Thought Prompting
- Slower Responses—Chain of Thought (CoT) prompting makes AI think step by step, which can make answers longer and slower. Instead of giving a quick reply, the AI takes more time to explain its reasoning.
- More Mistakes in Long Answers – Even though CoT helps the AI think carefully, longer reasoning chains can lead to more mistakes. If one step is wrong, the entire answer might be incorrect.
- Needs More Computing Power – CoT prompting makes AI process more information, which requires more computer resources. This can slow down responses and make it expensive to run.
- Not Always Needed – Some simple problems do not require step-by-step reasoning. Using CoT in these cases can make answers unnecessarily complicated instead of clear and direct.
- Still Limited by AI’s Knowledge—CoT does not improve AI knowledge. If the AI does not have the right data, breaking down the problem into steps will not correct the answer.
- Difficult to Control—Sometimes, CoT prompts cause the AI to overexplain or go off-topic. The AI may add too much detail or provide extra steps that are not useful.
- Harder for Beginners – If someone is new to AI, understanding long explanations from CoT can be confusing. Simple answers may be better for them.
FAQs
1. What is Chain of Thought (CoT) prompting, and how does it work?
Chain of Thought (CoT) prompting is a way to help AI think step by step. Instead of giving quick answers, AI explains its thought process before concluding. This helps avoid mistakes. For example, in math problems, AI first breaks the problem into smaller parts before solving it.
2. How does CoT prompting improve LLM reasoning?
CoT prompting makes AI smarter by forcing it to think in steps and prevents it from making random guesses. By explaining its reasoning, AI can solve complex problems better, such as math, logic puzzles, and decision-making tasks. This makes its answers more accurate and easy to understand.
3. What are practical CoT prompting examples?
CoT prompting is useful in many areas. In math, AI solves equations step by step. In coding, AI plans before writing code. In decision-making, AI checks all facts before suggesting solutions. It is also used in answering tricky questions and solving logic puzzles more accurately.
4. How do I code CoT prompting in Python?
To use CoT prompting in Python, you can structure AI prompts to think in steps. If using OpenAI’s API, you can write:
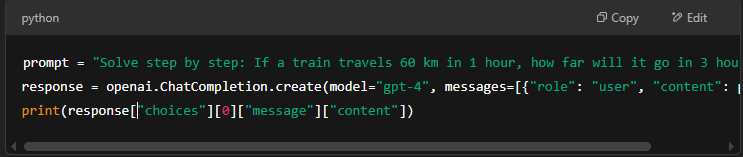
This makes AI explain its reasoning before answering.
5. How does CoT compare to other prompting methods?
CoT is better than direct prompting because it encourages step-by-step thinking. Unlike basic prompting, which asks AI to give quick answers, CoT forces AI to explain its process, making answers more reliable. Compared to zero-shot prompting, CoT helps in complex reasoning tasks like math and decision-making.